PCA 手写主成分分析
1 | import numpy as np |
| 5.1 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 1 | 4.7 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 2 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 3 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 4 | 5.4 | 3.9 | 1.7 | 0.4 | Iris-setosa |
1 数据预处理
1 | #加上列名 |
| sepal_len | sepal_wid | petal_len | petal_wid | class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 1 | 4.7 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 2 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 3 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 4 | 5.4 | 3.9 | 1.7 | 0.4 | Iris-setosa |
2 画图,进行降维特征分析
1 | # split data table into data X and class labels y |
1 | # 把每个特征用于分类的结果,都画成条形图,观察哪个特征更容易划分种类 |
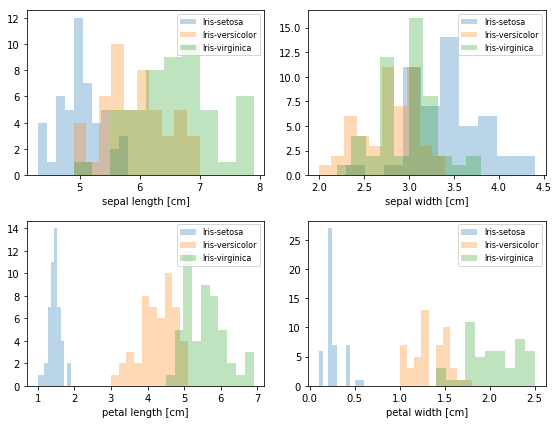
1 | # 特征 归一化 |
3 协方差分析(发现有2个有用特征,决定从4维降到2维)
1 计算样本X的 协方差矩阵(有4个特征,所以是4x4)
1 | # 自己算 协方差矩阵 |
Covariance matrix
[[ 1.00675676 -0.10448539 0.87716999 0.82249094]
[-0.10448539 1.00675676 -0.41802325 -0.35310295]
[ 0.87716999 -0.41802325 1.00675676 0.96881642]
[ 0.82249094 -0.35310295 0.96881642 1.00675676]]
1 | # numpy算 协方差矩阵 |
NumPy covariance matrix:
[[ 1.00675676 -0.10448539 0.87716999 0.82249094]
[-0.10448539 1.00675676 -0.41802325 -0.35310295]
[ 0.87716999 -0.41802325 1.00675676 0.96881642]
[ 0.82249094 -0.35310295 0.96881642 1.00675676]]
2 对协方差矩阵进行 特征值分解
1 | cov_mat = np.cov(X_std.T) |
Eigenvectors
[[ 0.52308496 -0.36956962 -0.72154279 0.26301409]
[-0.25956935 -0.92681168 0.2411952 -0.12437342]
[ 0.58184289 -0.01912775 0.13962963 -0.80099722]
[ 0.56609604 -0.06381646 0.63380158 0.52321917]]
Eigenvalues
[ 2.92442837 0.93215233 0.14946373 0.02098259]
3 把特征值从大到小排列,并配对特征向量
1 | # Make a list of (eigenvalue, eigenvector) tuples |
[(2.9244283691111144, array([ 0.52308496, -0.25956935, 0.58184289, 0.56609604])), (0.93215233025350641, array([-0.36956962, -0.92681168, -0.01912775, -0.06381646])), (0.14946373489813314, array([-0.72154279, 0.2411952 , 0.13962963, 0.63380158])), (0.020982592764270606, array([ 0.26301409, -0.12437342, -0.80099722, 0.52321917]))]
----------
Eigenvalues in descending order:
2.92442836911 对应 [ 0.52308496 -0.25956935 0.58184289 0.56609604]
0.932152330254 对应 [-0.36956962 -0.92681168 -0.01912775 -0.06381646]
0.149463734898 对应 [-0.72154279 0.2411952 0.13962963 0.63380158]
0.0209825927643 对应 [ 0.26301409 -0.12437342 -0.80099722 0.52321917]
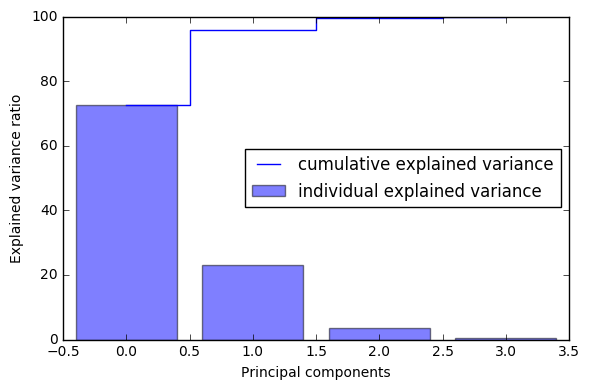
4 通过前面特征值累加所占比重 的图像,判断取前多少特征值合适,组成投影矩阵W
1 | tot = sum(eig_vals) |
[72.620033326920336, 23.147406858644135, 3.7115155645845164, 0.52104424985101538]
array([ 72.62003333, 95.76744019, 99.47895575, 100. ])
1 | a = np.array([1,2,3,4]) |
[1 2 3 4]
-----------
[ 1 3 6 10]
1 |
|
1 | matrix_w = np.hstack((eig_pairs[0][1].reshape(4,1), |
Matrix W:
[[ 0.52308496 -0.36956962]
[-0.25956935 -0.92681168]
[ 0.58184289 -0.01912775]
[ 0.56609604 -0.06381646]]
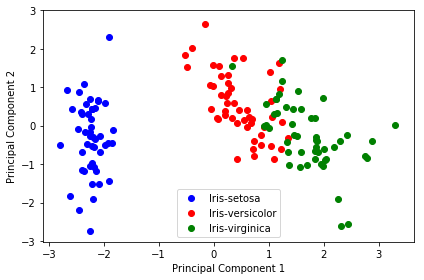
4 开始降维——用投影矩阵降维样本矩阵X
1 | Y = X_std.dot(matrix_w) |
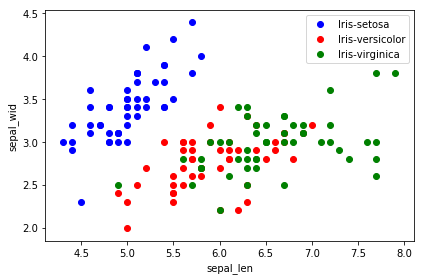
5 画图观察 降维前 和 降维后的样本分布
1 | plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4)) |
1 | plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4)) |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |